Goal that minimizes marker acceleration in a Moco optimization problem. More...
#include <MocoMarkerAccelerationGoal.h>
Public Member Functions | |
| void | setMarkerName (std::string name) |
| Set the name of the marker whose acceleration should be minimized. | |
| void | setMarkerName (std::string name) |
| Set the name of the marker to track. | |
| void | setExponent (int ex) |
| Set the exponent for the acceleration terms. | |
| bool | getExponent () const |
| Get the current exponent value. | |
| void | setDivideByDisplacement (bool tf) |
| Set whether to divide by displacement. | |
| bool | getDivideByDisplacement () const |
| Get whether the goal is divided by displacement. | |
Constructors | |
| MocoMarkerAccelerationGoal () | |
| Default constructor. | |
| MocoMarkerAccelerationGoal (std::string name) | |
| Constructor with name. | |
| MocoMarkerAccelerationGoal (std::string name, double weight) | |
| Constructor with name and weight. | |
| MocoMarkerAccelerationGoal () | |
| Default constructor. | |
| MocoMarkerAccelerationGoal (std::string name) | |
| Constructor with name. | |
| MocoMarkerAccelerationGoal (std::string name, double weight) | |
| Constructor with name and weight. | |
Protected Member Functions | |
Required implementations of virtual methods | |
| Mode | getDefaultModeImpl () const override |
| Get the default mode for this goal. | |
| void | initializeOnModelImpl (const Model &) const override |
| Initialize the goal with the model. | |
| void | calcIntegrandImpl (const IntegrandInput &input, SimTK::Real &integrand) const override |
| Calculate the integrand value for the cost function. | |
| void | calcGoalImpl (const GoalInput &input, SimTK::Vector &cost) const override |
| Calculate the goal value. | |
| Mode | getDefaultModeImpl () const override |
| Get the default mode for this goal. | |
| void | initializeOnModelImpl (const Model &) const override |
| Initialize the goal with the model. | |
| void | calcIntegrandImpl (const IntegrandInput &input, SimTK::Real &integrand) const override |
| Calculate the integrand value for the cost function. | |
| void | calcGoalImpl (const GoalInput &input, SimTK::Vector &cost) const override |
| Calculate the goal value. | |
Private Member Functions | |
| OpenSim_DECLARE_CONCRETE_OBJECT (MocoMarkerAccelerationGoal, MocoGoal) | |
| void | constructProperties () |
| Initialize the goal's properties. | |
| OpenSim_DECLARE_CONCRETE_OBJECT (MocoMarkerAccelerationGoal, MocoGoal) | |
| void | constructProperties () |
| Initialize the goal's properties. | |
Properties | |
| OpenSim_DECLARE_PROPERTY (exponent, int, "The exponent applied to the output value in the integrand. " "The output can take on negative values in the integrand when the " "exponent is set to 1 (the default value). When the exponent is " "set to a value greater than 1, the absolute value function is " "applied to the output (before the exponent is applied), meaning " "that odd numbered exponents (greater than 1) do not take on " "negative values.") | |
| OpenSim_DECLARE_PROPERTY (marker_name, std::string, "The name of the marker for this goal") | |
| OpenSim_DECLARE_PROPERTY (divide_by_displacement, bool, "Divide by the model's displacement over the phase (default: " "false)") | |
| OpenSim_DECLARE_PROPERTY (exponent, int, "The exponent applied to the output value in the integrand. " "The output can take on negative values in the integrand when the " "exponent is set to 1 (the default value). When the exponent is " "set to a value greater than 1, the absolute value function is " "applied to the output (before the exponent is applied), meaning " "that odd numbered exponents (greater than 1) do not take on " "negative values.") | |
| OpenSim_DECLARE_PROPERTY (marker_name, std::string, "The name of the marker for this goal") | |
Private Attributes | |
Internal working variables | |
| std::function< double(const double &)> | m_power_function |
| SimTK::ReferencePtr< const Point > | m_model_marker |
| Reference to the marker in the model. | |
Detailed Description
Goal that minimizes marker acceleration in a Moco optimization problem.
Goal that minimizes the acceleration of a model marker.
This goal minimizes the absolute acceleration of a model marker summed over its x, y, and z components, integrated over the phase. The integrand is:
![\[
|\ddot{p}|^p = (|\ddot{p}_x| + |\ddot{p}_y| + |\ddot{p}_z|)^p
\]](form_6.png)
where 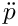
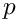
This goal can be useful for:
- Reducing rapid changes in marker motion
- Smoothing marker trajectories
- Minimizing jerk in marker paths
- Note
- The marker must exist in the model and its name must be specified using setMarkerName() before the goal can be used.
This goal minimizes the absolute acceleration of a specified model marker, integrated over the phase. The acceleration is computed as the sum of the squared accelerations in the x, y, and z directions.
This goal can be useful for:
- Generating smoother marker trajectories
- Reducing rapid changes in marker motion
- Minimizing jerk in specific body segments
- Improving motion naturalness
The goal requires specification of a marker name to track. The acceleration can be raised to a specified power using the exponent property, and can optionally be divided by the total displacement of the model during the phase to make the cost invariant to the distance traveled.
Constructor & Destructor Documentation
◆ MocoMarkerAccelerationGoal() [1/6]
|
inline |
Default constructor.
◆ MocoMarkerAccelerationGoal() [2/6]
|
inline |
Constructor with name.
- Parameters
-
name The name of the goal
◆ MocoMarkerAccelerationGoal() [3/6]
|
inline |
Constructor with name and weight.
- Parameters
-
name The name of the goal weight Weight for this goal term in the optimization
◆ MocoMarkerAccelerationGoal() [4/6]
|
inline |
Default constructor.
◆ MocoMarkerAccelerationGoal() [5/6]
|
inline |
Constructor with name.
- Parameters
-
name The name of the goal
◆ MocoMarkerAccelerationGoal() [6/6]
|
inline |
Constructor with name and weight.
- Parameters
-
name The name of the goal weight Weight for this goal term in the optimization
Member Function Documentation
◆ calcGoalImpl() [1/2]
|
overrideprotected |
Calculate the goal value.
- Parameters
-
input Input data containing the integral cost Vector to store the calculated cost
◆ calcGoalImpl() [2/2]
|
overrideprotected |
Calculate the goal value.
- Parameters
-
input Input data containing the integral cost Vector to store the calculated cost
◆ calcIntegrandImpl() [1/2]
|
overrideprotected |
Calculate the integrand value for the cost function.
- Parameters
-
input Input data for the current state integrand Reference to store the calculated integrand value
◆ calcIntegrandImpl() [2/2]
|
overrideprotected |
Calculate the integrand value for the cost function.
- Parameters
-
input Input data for the current state integrand Reference to store the calculated integrand value
◆ constructProperties() [1/2]
|
private |
Initialize the goal's properties.
◆ constructProperties() [2/2]
|
private |
Initialize the goal's properties.
◆ getDefaultModeImpl() [1/2]
|
inlineoverrideprotected |
Get the default mode for this goal.
◆ getDefaultModeImpl() [2/2]
|
inlineoverrideprotected |
Get the default mode for this goal.
◆ getDivideByDisplacement()
|
inline |
Get whether the goal is divided by displacement.
- Returns
- True if divided by displacement, false otherwise
◆ getExponent()
|
inline |
Get the current exponent value.
- Returns
- The exponent value
◆ initializeOnModelImpl() [1/2]
|
overrideprotected |
Initialize the goal with the model.
◆ initializeOnModelImpl() [2/2]
|
overrideprotected |
Initialize the goal with the model.
◆ OpenSim_DECLARE_CONCRETE_OBJECT() [1/2]
|
private |
◆ OpenSim_DECLARE_CONCRETE_OBJECT() [2/2]
|
private |
◆ OpenSim_DECLARE_PROPERTY() [1/5]
|
private |
◆ OpenSim_DECLARE_PROPERTY() [2/5]
|
private |
◆ OpenSim_DECLARE_PROPERTY() [3/5]
|
private |
◆ OpenSim_DECLARE_PROPERTY() [4/5]
|
private |
◆ OpenSim_DECLARE_PROPERTY() [5/5]
|
private |
◆ setDivideByDisplacement()
|
inline |
Set whether to divide by displacement.
- Parameters
-
tf True to divide by displacement, false otherwise
◆ setExponent()
|
inline |
Set the exponent for the acceleration terms.
- Parameters
-
ex The exponent value
◆ setMarkerName() [1/2]
|
inline |
Set the name of the marker whose acceleration should be minimized.
- Parameters
-
name Name of the marker in the model
◆ setMarkerName() [2/2]
|
inline |
Set the name of the marker to track.
- Parameters
-
name The marker name
Member Data Documentation
◆ m_model_marker
|
mutableprivate |
Reference to the marker in the model.
Reference to the model marker being tracked.
◆ m_power_function
|
mutableprivate |
Function to compute power of acceleration values
The documentation for this class was generated from the following files:
- F:/dev/projects/MocoExtendProblem/custom_goals/MocoMarkerAccelerationGoal/MocoMarkerAccelerationGoal.h
- F:/dev/projects/MocoExtendProblem/custom_goals_compat/MocoMarkerAccelerationGoal/MocoMarkerAccelerationGoal.h
- F:/dev/projects/MocoExtendProblem/custom_goals/MocoMarkerAccelerationGoal/MocoMarkerAccelerationGoal.cpp
- F:/dev/projects/MocoExtendProblem/custom_goals_compat/MocoMarkerAccelerationGoal/MocoMarkerAccelerationGoal.cpp
Generated by